Code LOVE20 applied for 20% off!

Subtotal
$0
U.S. Shipping
FREE
Saved for Later
Shopping Cart

Code LOVE20 applied for 20% off!

Subtotal
$0
U.S. Shipping
FREE
Saved for Later
Vincent Van Gogh was born the second of six children into a religious Dutch Reformed Church family in the south of the Netherlands. His father, Theodorus Van Gogh, was a clergyman and his mother, Anna Cornelia Carbentus, was the daughter of a bookseller. Van Gogh exhibited unstable moods during his childhood, and showed no early inclination toward art-making, though he excelled at languages while attending two boarding schools. In 1868, he abandoned his studies and never successfully returned to formal schooling.
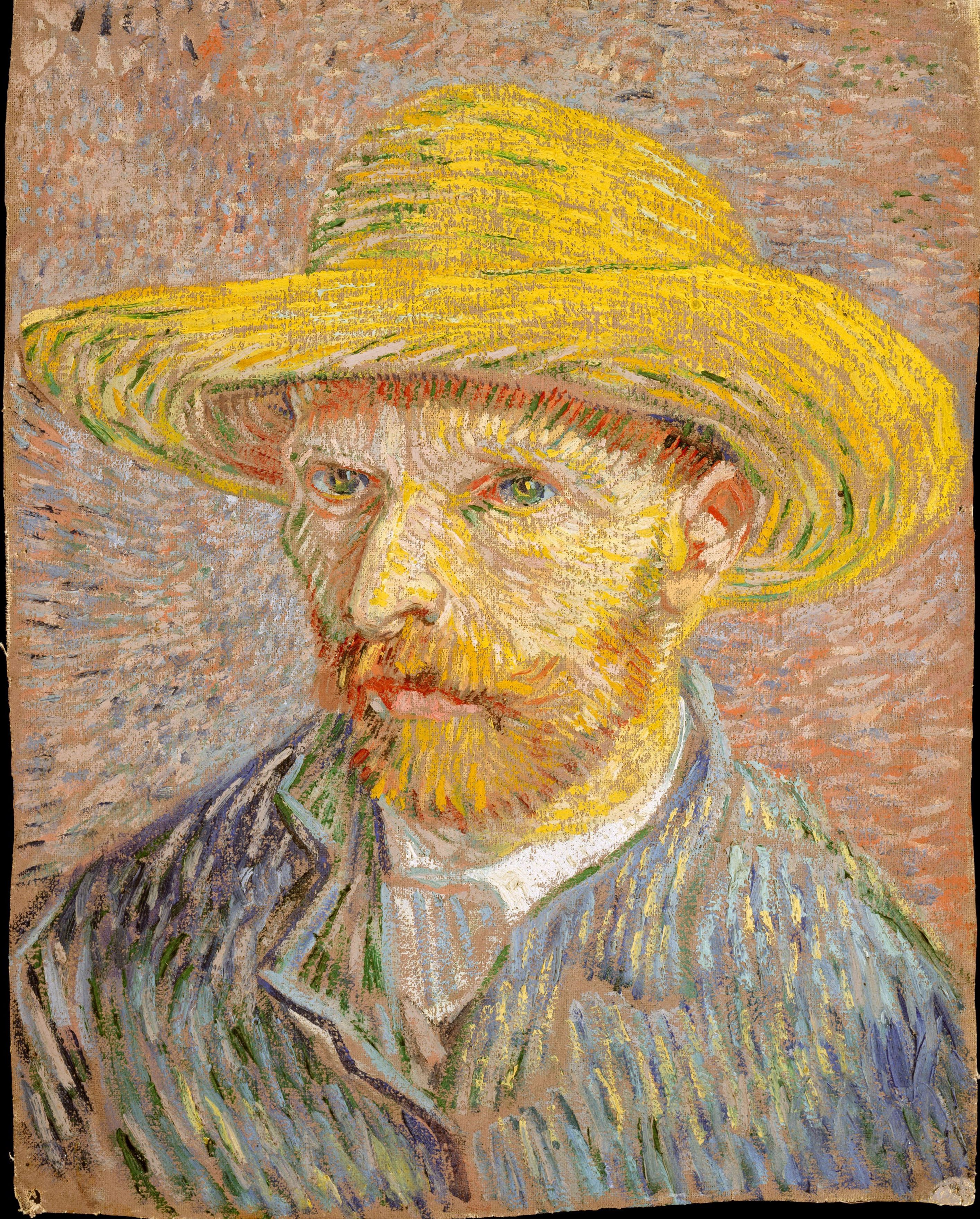

Self-Portrait With A Straw Hat by Vincent van Gogh
In 1869, Van Gogh apprenticed at the headquarters of the international art dealers Goupil & Cie in Paris and eventually worked at the Hague branch of the firm. He was relatively successful as an art dealer and stayed with the firm for almost a decade. In 1872, Van Gogh began exchanging letters with his younger brother Theo. This correspondence continued through the end of Vincent's life. The following year, Theo himself became an art dealer, and Vincent was transferred to the London office of Goupil & Cie. Around this time, Vincent became depressed and turned to God.
After several transfers between London and Paris, Van Gogh was let go from his position at Goupil's and decided to pursue a life in the clergy. While living in southern Belgium as a poor preacher, he gave away his possessions to the local coal-miners until the church dismissed him because of his overly enthusiastic commitment to his faith. In 1880, Van Gogh decided he could be an artist and still remain in God's service, writing, "To try to understand the real significance of what the great artists, the serious masters, tell us in their masterpieces, that leads to God; one man wrote or told it in a book; another, in a picture." Van Gogh was still a pauper, but Theo sent him some money for survival. Theo financially supported his elder brother his entire career, as Vincent made virtually no money from making art.
A year later, in 1881, dire poverty motivated Van Gogh to move back home with his parents, where he taught himself to draw. He became infatuated with his cousin, Kee Vos-Stricker. His continued pursuit of her affection, despite utter rejection, eventually split the family. With the support of Theo, Van Gogh moved to the Hague, rented a studio, and studied under Anton Mauve - a leading member of the Hague School. Mauve introduced Van Gogh to the work of the French painter Jean-François Millet, who was renowned for depicting common laborers and peasants.
In 1884, after moving to Nuenen, Netherlands, Van Gogh began drawing the weathered hands, heads, and other anatomical features of workers and the poor, determined to become a painter of peasant life like Millet. Although he found a professional calling, his personal life was in shambles. Van Gogh accused Theo of not trying hard enough to sell his paintings, to which Theo replied that Vincent's dark palette was out of vogue compared to the bold and bright style of the Impressionist artists that was popular. Suddenly, on March 26, 1885, their father died from a stroke, putting pressure on Van Gogh to have a successful career. Shortly afterward, he completed the Potato Eaters (1885), his first large-scale composition and great work.
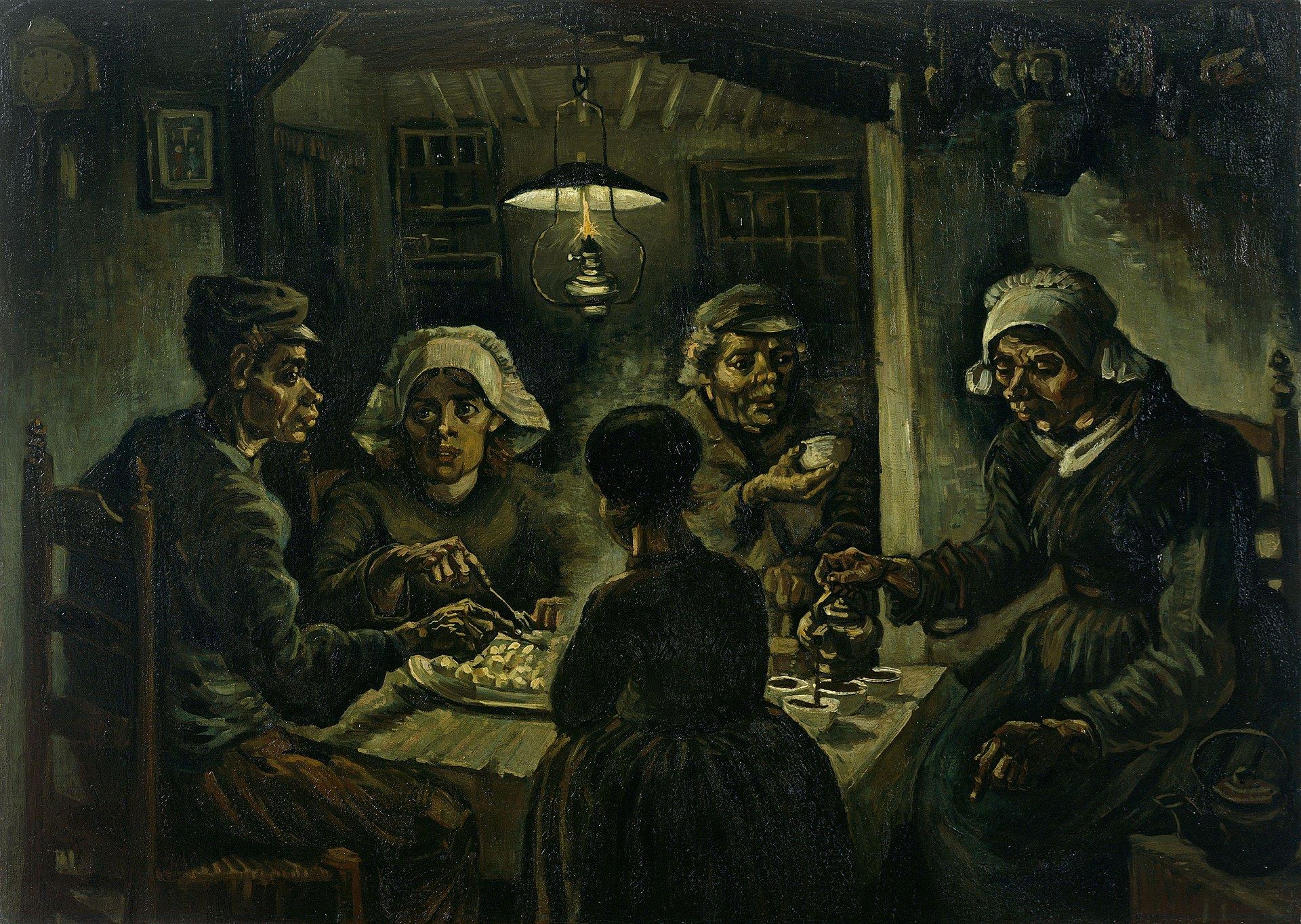

Potato Eaters by Vincent van Gogh
Leaving the Netherlands for the last time, in 1885 Van Gogh enrolled at the Academy of Fine Arts in Antwerp. There he discovered the art of Baroque painter Peter Paul Rubens, whose swirling forms and loose brushwork had a clear impact on the young artist's style. However, the rigidity of academicism of the school did not appeal to Van Gogh and he left for Paris the following year. He moved in with Theo in Montmartre - the artist's district in northern Paris - and studied with painter Fernand Cormon, who introduced the young artist to the Impressionists. The influence of artists such as Claude Monet, Camille Pissarro, Edgar Degas, and Georges Seurat, as well as pressure from Theo to sell paintings, motivated Van Gogh to adopt a lighter palette.
From 1886 to 1888, Van Gogh became acutely interested in Japanese prints and began to avidly study and collect them, even curating an exhibition of them at a Parisian restaurant. In late 1887, Van Gogh organized an exhibition that included his work and that of his colleagues Emile Bernard and Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, and in early 1888, he exhibited with the Neo-impressionists Georges Seurat and Paul Signac at the Salle de Repetition of the Theatre Libre d'Antoine.

Almond Blossom by Vincent van Gogh
The majority of Van Gogh's best-known works were produced during the final two years of his life. During the fall and winter of 1888, Vincent Van Gogh and Paul Gauguin lived and worked together in Arles in the south of France, where Van Gogh eventually rented four rooms at 2 Place Lamartine, which was dubbed the "Yellow House" for its citron hue. The move to Provence began as a plan for a new artist's community in Arles as an alternative to Paris and came at a critical point in each of the artists' careers. While at the "Yellow House" Gauguin and Van Gogh worked closely together and developed a concept of color symbolic of inner emotion and not dependent upon nature. Despite enormous productivity, Van Gogh suffered from various bouts of mental instability, likely including epilepsy, psychotic episodes, delusions, and bipolar disorder. Gauguin left for Tahiti, partially as a means of escaping Van Gogh's increasingly erratic behavior. The artist slipped away after a particularly violent fight in which Van Gogh threatened Gauguin with a razor and then cut off part of his own right ear.
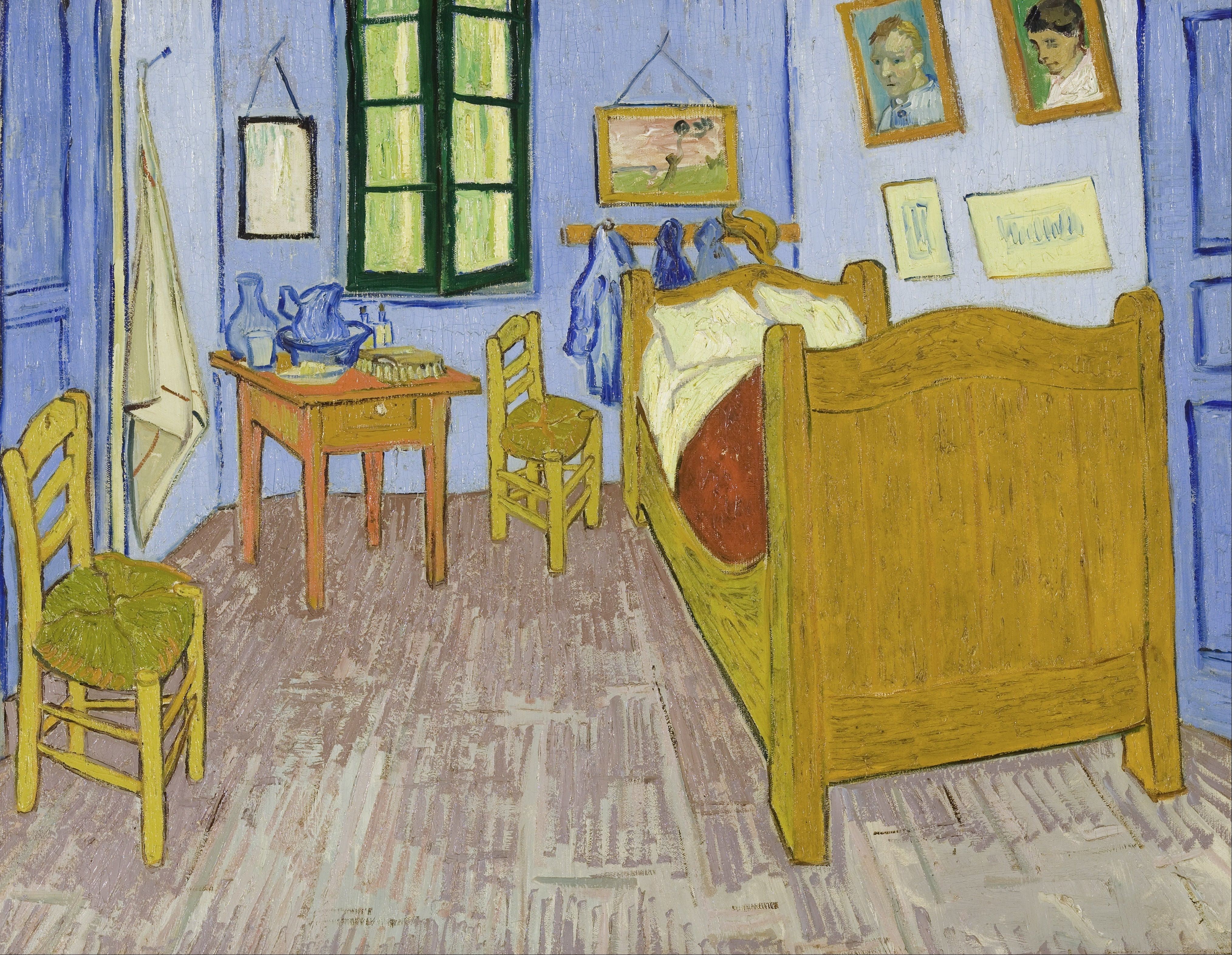

The Bedroom by Vincent van Gogh
On May 8, 1889, reeling from his deteriorating mental condition, Van Gogh voluntarily committed himself into a psychiatric institution in Saint-Remy, near Arles. As the weeks passed, his mental well-being remained stable and he was allowed to resume painting. This period became one of his most productive. In the year spent at Saint-Remy, Van Gogh created over 100 works, including Starry Night (1889). The clinic and its garden became his main subjects, rendered in the dynamic brushstrokes and lush palettes typical of his mature period. On his walks around the grounds, Van Gogh immersed himself in the experience of the natural surroundings, later recreating from memory the olive and cypress trees, irises, and other flora that populated the clinic's campus.
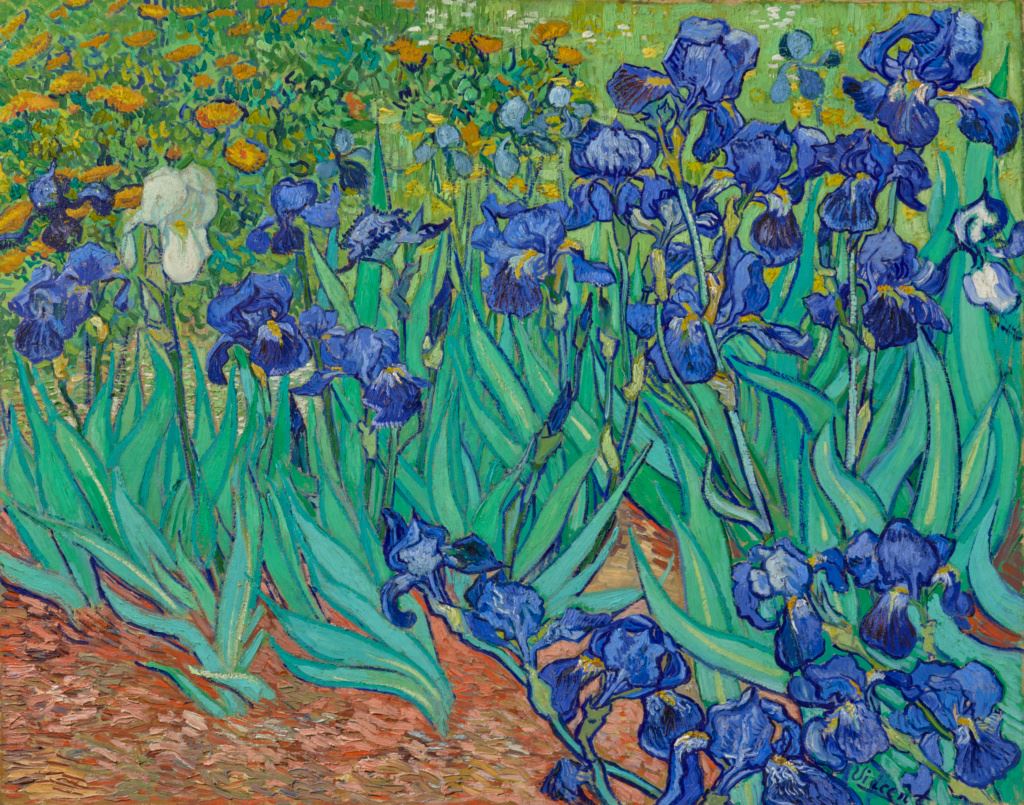

Irises by Vincent van Gogh
Shortly after leaving the clinic, Van Gogh moved north to Auvers-sur-Oise outside of Paris, to the care of a homeopathic doctor and amateur artist, Dr. Gachet. The doctor encouraged Van Gogh to paint as part of his recovery, and he happily obliged. He avidly documented his surroundings in Auvers, averaging roughly a painting a day over the last months of his life. However, after Theo disclosed his plan to go into business for himself and explained funds would be short for a while, Van Gogh's depression deepened sharply. On July 27, 1890, he wandered into a nearby wheat field and reputably shot himself in the chest with a revolver. Although Van Gogh managed to struggle back to his room, his wounds were not treated properly and he died in bed two days later. Theo rushed to be at his brother's side during his last hours and reported that his final words were: "The sadness will last forever."
Clear examples of Van Gogh's wide influence can be seen throughout art history. The Fauves and the German Expressionists worked immediately after Van Gogh and adopted his subjective and spiritually inspired use of color. The Abstract Expressionists of the mid-20th century made use of Van Gogh's technique of sweeping, expressive brushstrokes to indicate the artist's psychological and emotional state. Even the Neo-Expressionists of the 1980s, like Julian Schnabel and Eric Fischl, owe a debt to Van Gogh's expressive palette and brushwork. In popular culture, his life has inspired music and numerous films, including Vincente Minelli's Lust for Life (1956), which explores Van Gogh and Gauguin's volatile relationship. In his lifetime, Van Gogh created 900 paintings and made 1,100 drawings and sketches, but only sold one painting during his career. With no children of his own, most of Van Gogh's works were left to brother Theo. While he was not a success in his lifetime, Van Gogh was an enormous success after his death. Contemporary impressionists like Erin Hanson cite Van Gogh as an influential figure in their artistic journey. No doubt, Van Gogh will continue to inspire for centuries to come.

Sedona Irises by Erin Hanson
Credit: Article reproduced with permission from theartstory.org
Reference: https://www.theartstory.org/artist/van-gogh-vincent/life-and-legacy/#nav
Discover the artist at the forefront of modern impressionism.
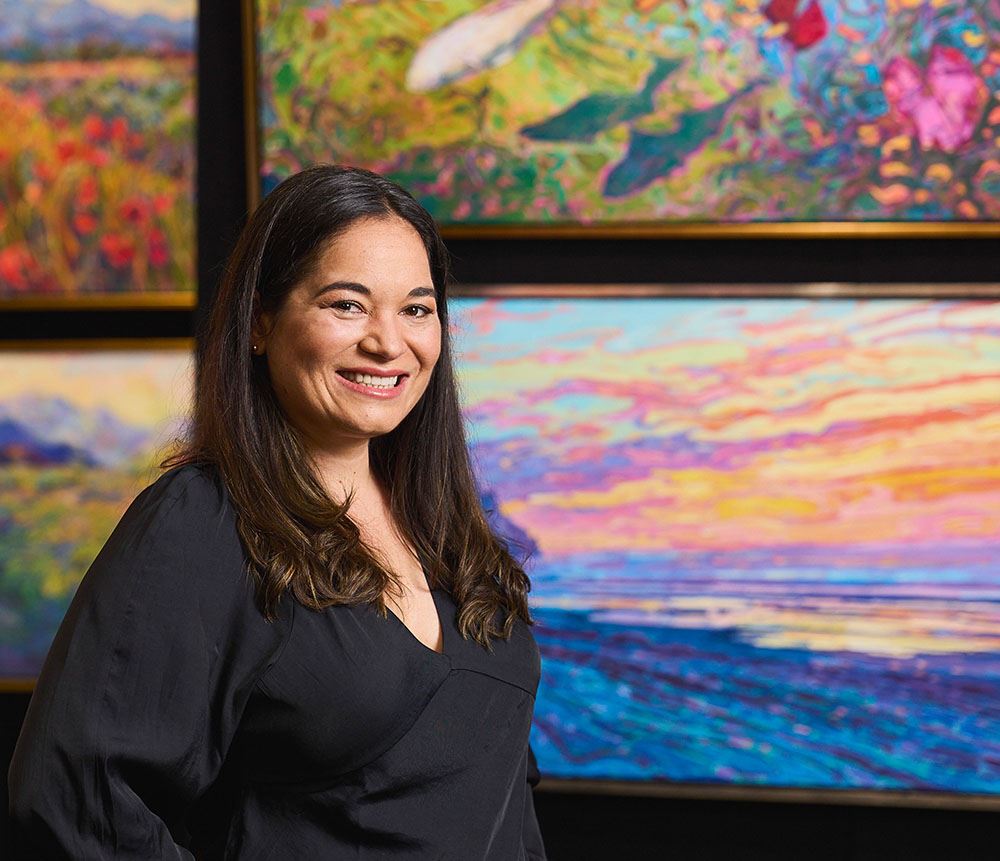
About Erin
ERIN HANSON has been painting in oils since she was 8 years old. As a teenager, she apprenticed at a mural studio where she worked on 40-foot-long paintings while selling art commissions on the side. After being told it was too hard to make a living as an artist, she got her degree in Bioengineering from UC Berkeley. Afterward, Erin became a rock climber at Red Rock Canyon, Nevada. Inspired by the colorful scenery she was climbing, she decided to return to her love of painting and create one new painting every week.
She has stuck to that decision, becoming one of the most prolific artists in history, with over 3,000 oil paintings sold to eager collectors. Erin Hanson’s style is known as "Open Impressionism" and is taught in art schools worldwide. With millions of followers, Hanson has become an iconic, driving force in the rebirth of impressionism, inspiring thousands of other artists to pick up the brush.